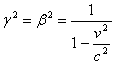Lorentz Transformation from First Principles
The conversion from the Galilean transformation to the relativistic transformation has some mixing of time and space variables.
![]() (1)
(1)
where g, b, and a are presently unknown.
We can always invoke the constancy of the speed of light and let x=ct and x’=ct’ and substitute these into equations 1 to get some information on the relationships between g, b, and a.
![]() (1a)
(1a)
![]()
![]() (1b)
(1b)
The condition that there be no special frame requires that the inverse transform’s only difference is that v->-v (and, as it will turn out, a->-a).
![]() (2)
(2)
We cans also solve equations 1 for x and t:
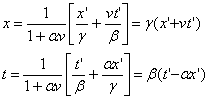 (3)
(3)
From the first equation, setting the coefficients of x’ equal, we get:
![]()
and from the second equation setting the coefficients of t’ equal we get:
![]()
From which we conclude that g=b.
Now, using equation 1b we have:
![]()
so that
![]()
and thus